Bariatric Surgery For Weight Loss: Types, Risks, and Benefits
Obesity is a serious health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic condition that can lead to various health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. For people who are unable to lose weight through diet and exercise, bariatric surgery can be an effective solution. In this article, we will discuss what bariatric surgery is, why it's done, the types of bariatric surgery, who it's for, the risks involved, and how to prepare for the operation.
What is "Bariatric Surgery"?
Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, is a surgical procedure that helps people lose weight by restricting the amount of food they can eat or by reducing the absorption of nutrients. Bariatric surgery is usually recommended for people who have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or for those who have a BMI of 35 or higher with comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea.
Why it's done?
Bariatric surgery is done to help people lose weight and improve their health. Obesity is a major risk factor for several health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. Weight loss surgery can help reduce or eliminate these risks and improve overall health.
Is bariatric surgery a big operation?
Bariatric surgery is a major operation that requires general anesthesia and typically takes several hours to complete. The specific type of surgery will determine the length of the operation. Patients will need to stay in the hospital for a few days after the surgery and will need to follow a strict diet and exercise plan to ensure a successful recovery.
Is bariatric surgery only for obesity?
While bariatric surgery is primarily used to treat obesity, it can also be used to treat other conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (Bariatric Surgery ), type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure. Bariatric surgery has been shown to be effective in improving or resolving many obesity-related health conditions.
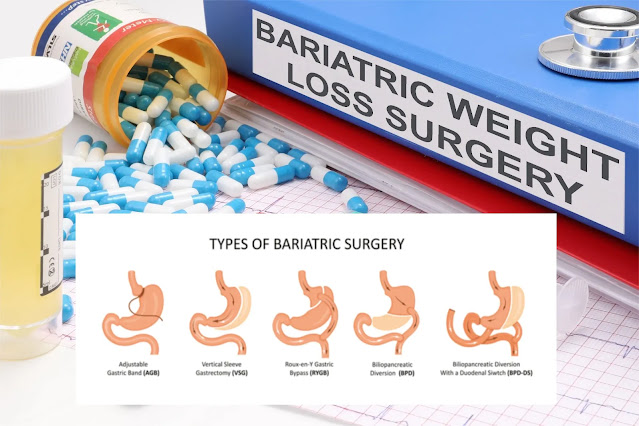
What are the types of "Bariatric Surgery"?
There are several types of bariatric surgery, including:
Gastric bypass surgery: This procedure involves creating a small pouch in the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to the pouch. This limits the amount of food a person can eat and reduces the absorption of nutrients.
Sleeve gastrectomy: This procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach and creating a smaller, banana-shaped stomach. This limits the amount of food a person can eat and reduces the production of the hunger hormone ghrelin.
Adjustable gastric banding: This procedure involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a smaller pouch. The band can be adjusted to control the amount of food a person can eat.
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch: This procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to the remaining portion of the stomach. This limits the amount of food a person can eat and reduces the absorption of nutrients.
Which bariatric surgery is safe?
All types of bariatric surgery have risks and benefits, and the safety of a particular type of surgery depends on the individual patient. The decision to undergo bariatric surgery should be made after careful consideration and consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. However, gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy are generally considered to be the safest and most effective types of bariatric surgery.
Who is "Bariatric Surgery" for?
Bariatric surgery is recommended for people who have a BMI of 40 or higher, or for those who have a BMI of 35 or higher with comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea. Candidates for bariatric surgery should also have tried other weight loss methods, such as diet and exercise, without success.
What are the Risks of "Bariatric Surgery"?
Bariatric surgery is a major operation and carries risks, including infection, bleeding, blood clots, and anesthesia complications. Other risks include dumping syndrome (a condition where food moves too quickly through the digestive system), bowel obstruction, and hernias. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of bariatric surgery with their healthcare provider before making a decision.
How to prepare for the operation?
Preparing for bariatric surgery involves several steps, including:
Consultation with a healthcare provider: Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine if they are a good candidate for bariatric surgery.
Preoperative testing: Patients may need to undergo several tests, such as blood tests, imaging tests, and electrocardiograms.
Diet and exercise: Patients will need to follow a strict diet and exercise plan before the surgery to prepare their body for the procedure.
Quit smoking: Patients who smoke will need to quit smoking before the surgery to reduce the riskof complications.
Mental health evaluation: Patients may need to undergo a mental health evaluation to ensure they are psychologically prepared for the surgery and the lifestyle changes that come with it.
What you can expect?
After bariatric surgery, patients can expect to lose a significant amount of weight and improve their overall health. However, the recovery process can be challenging, and patients will need to follow a strict diet and exercise plan to ensure a successful outcome. Patients may also experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea in the first few weeks after surgery.
After bariatric surgery, What is the bariatric diet?
The bariatric diet is a diet plan that is designed to help patients recover from bariatric surgery and achieve their weight loss goals. The diet typically consists of several stages, starting with a liquid diet immediately after surgery, followed by a pureed diet, soft foods, and finally, solid foods. Patients will need to follow the bariatric diet for several months after surgery to ensure a successful recovery.
Improving weight and general health
Bariatric surgery can help patients improve their weight and overall health. In addition to weight loss, bariatric surgery has been shown to improve or resolve many obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. However, bariatric surgery is not a quick fix, and patients will need to make significant lifestyle changes to maintain their weight loss and improve their health long-term.
When weight-loss surgery doesn't work
While bariatric surgery can be an effective solution for weight loss, it is not always successful. In some cases, patients may not achieve their desired weight loss goals or may experience weight regain after surgery. In these cases, patients may need to undergo revision surgery or explore other weight loss options, such as diet and exercise or medication.
In conclusion, bariatric surgery can be an effective solution for weight loss and improving overall health for people who have struggled with obesity and related health conditions. However, it is a major operation that carries risks and requires significant lifestyle changes to maintain weight loss and improve health long-term. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of bariatric surgery with their healthcare provider and carefully consider their options before making a decision.
References:
American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. (2021). Benefits of Weight Loss Surgery. Retrieved from https://asmbs.org/patients/benefits-of-weight-loss-surgery
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Bariatric surgery. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/bariatric-surgery/about/pac-20394258
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2020). Bariatric Surgery Procedures. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/bariatric-surgery/bariatric-surgery-procedures
Nguyen, N. T., Varela, J. E. (2016). Bariatric surgery for obesity and metabolic disorders: state of the art. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 14(3), 160-169. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.170
Puzziferri, N., Roshek, T. B., Mayo, H. G., Gallagher, R., Belle, S. H., Livingston, E. H. (2014). Long-term follow-up after bariatric surgery: a systematic review. JAMA, 312(9), 934-942. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.10706







0 Comments